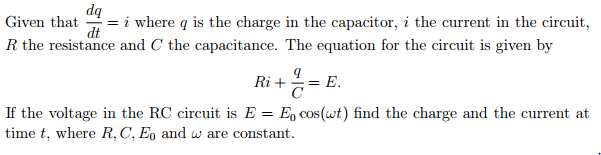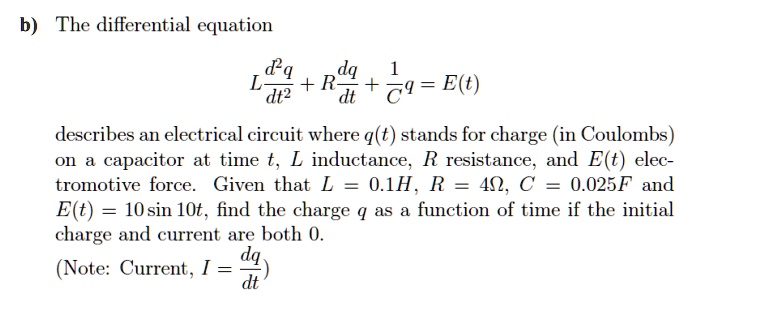
SOLVED: The differential equation dq/dt + Rdq/dt + 3q = E(t) describes an electrical circuit where q(t) stands for charge (in Coulombs) on a capacitor at time t, L stands for inductance,

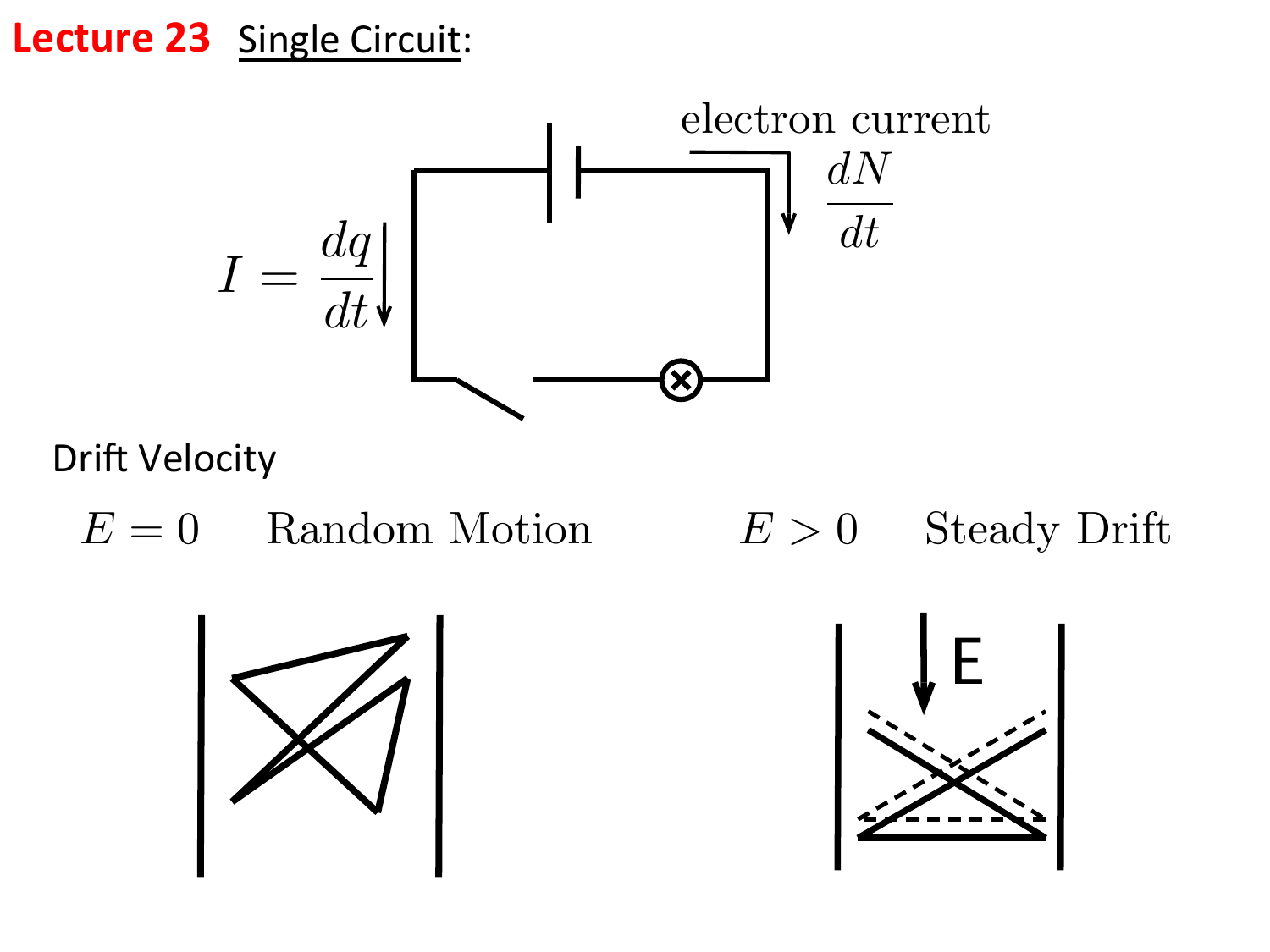
Introduction to Current In AP C Current I = dq/dt I: current in Amperes (A) q: charge in Coulombs (C) t: time in seconds (s) - ppt download

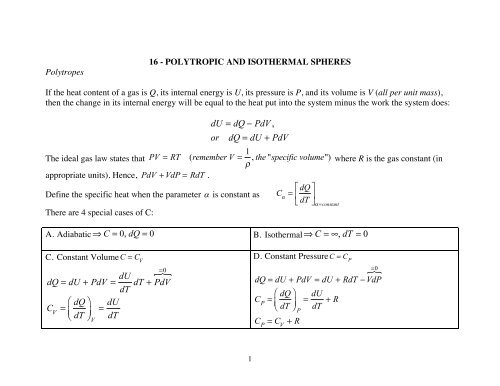
SOLVED: The 1st Law of Thermodynamics can be written in the differential form dQ = dU + PdV by expressing dU in terms of dT and dV. Show that dQ = Cp

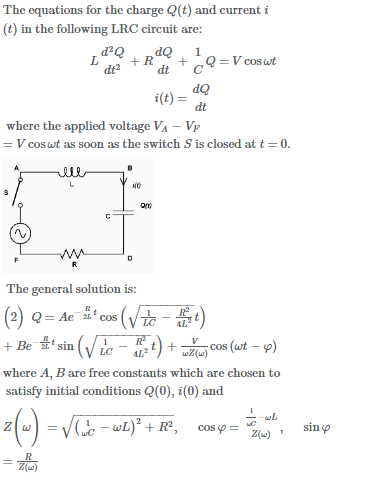
SOLVED: The charge q(t) on a capacitor in an LRC-Series Circuit satisfies the second-order differential equation: d^2q/dt^2 + R*(dq/dt) + (1/(LC))*q = E(t) Where L is the inductance, R is the resistance,

The temperature (T) dependences of the (a) Q, (b) dQ dT , (c) < (δQ) 2... | Download Scientific Diagram
The current i and charge q in a series circuit containing an inductance L, capacitance C e.m.f E satisfy the D.E. Ldi/dt + q/C = E, i = dq/dt· - Sarthaks eConnect

Using ε = - dϕ/dt and ε = iR find the current in the loop after the external field has stopped changing.

Results obtained for an 18 °C foam: instantaneous heat energy dQ/dt (W)... | Download Scientific Diagram

Heat absorption curves as a function of temperature on dQ/dT of the... | Download Scientific Diagram